This Dr. Axe content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure factually accurate information.
With strict editorial sourcing guidelines, we only link to academic research institutions, reputable media sites and, when research is available, medically peer-reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
This article is based on scientific evidence, written by experts and fact checked by our trained editorial staff. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to medically peer-reviewed studies.
Our team includes licensed nutritionists and dietitians, certified health education specialists, as well as certified strength and conditioning specialists, personal trainers and corrective exercise specialists. Our team aims to be not only thorough with its research, but also objective and unbiased.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
Top Vegan Omega-3 Sources & How to Get Into the Diet
October 27, 2022

There’s no doubt that omega-3 fatty acids are absolutely essential to health. It plays a role in nearly every aspect of health, with omega-3 benefits ranging from reduced inflammation to decreased bone loss, better brain function and beyond. Fish oil, cod liver oil, and fatty fish varieties like salmon, mackerel and tuna top the list of omega-3 fatty acid sources.
However, there are fewer vegan omega-3 sources to help meet your needs when following a plant-based diet, and even less omega-3 supplements are vegan.
Fortunately, there are plenty of ways to get a good amount of all three forms of omega-3 fatty acids into a plant-based diet, including docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and alpha-linolenic acid (ALA).
So how do vegans get omega-3? Do vegans need omega-3 supplements? And what vegan foods contain omega-3? Let’s take a closer look.
Top Foods
1. Brussels Sprouts
Brussels sprouts are undoubtedly one of the best omega-3 foods for a vegan diet. Not only does one cup of Brussels sprouts pack in over 87 milligrams of ALA, but it also contains other important nutrients, such as fiber, vitamin C and vitamin K. Cooked Brussels sprouts are even higher in omega-3 fatty acids, with 270 milligrams of ALA crammed into each cup. Best of all, they’re easy to enjoy and can be stir-fried, roasted or baked as a nutritious and delicious side dish to a well-rounded meal.
2. Algal Oil
Derived from algae and available in convenient supplement form, algal oil is one of very few vegan omega-3 DHA and EPA sources in the diet. Although the exact amounts can vary, algal oil supplements typically contain between 400–500 milligrams of combined EPA and DHA, delivering a good chunk of the omega-3 fatty acids you need for the entire day. One study published in the Journal of the American Dietetic Association also showed that algal oil is comparable to cooked salmon in terms of tolerance and absorption, making it a great alternative to fish oil.
3. Walnuts
Walnuts are one of the best vegan sources of omega-3 fatty acids as well as other healthy fats, including both poly- and monounsaturated fats. A single serving can meet and exceed your daily omega-3 fatty acid needs, providing a whopping 2,542 milligrams of ALA per ounce. Try upping your intake by sprinkling walnuts over yogurt, mixing them into homemade granola or enjoying a handful as is for a heart-healthy snack.
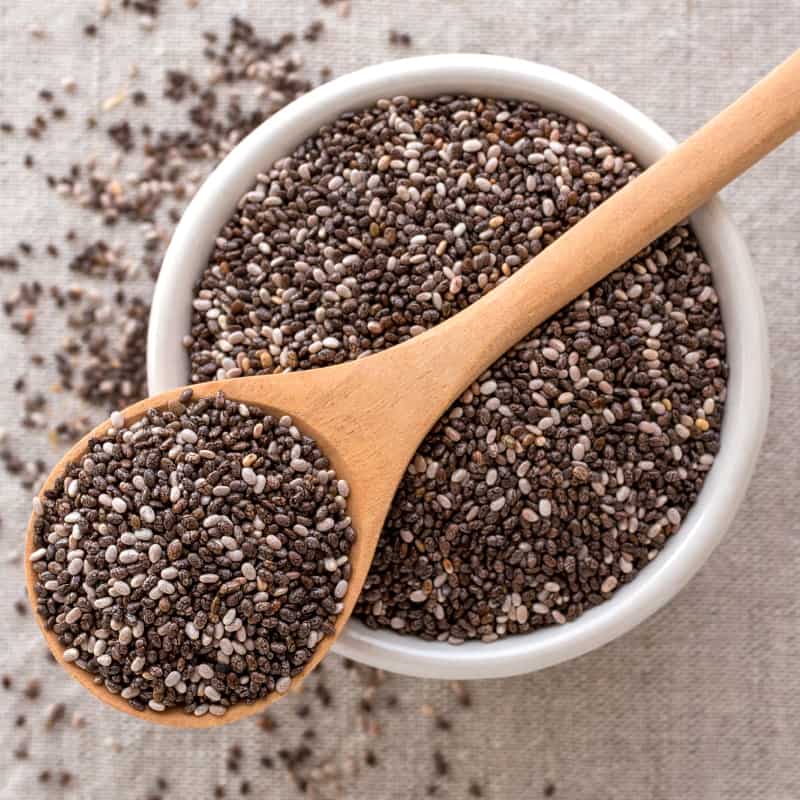
4. Chia Seeds
This nutritious vegan omega-3 source is as healthy as it is delicious. Just one ounce of chia seeds contains 4,915 milligrams of ALA, which is three times the daily recommended amount for men and four times the requirement for women. Chia seeds are also super convenient and can be easily incorporated into any diet by simply adding a scoop to yogurt, smoothies or puddings. You can even combine chia seeds with water and mix for an effective vegan egg substitute as well.
5. Perilla Oil
Perilla oil is a condiment commonly used in Korean cuisines that is made by extracting the oil from perilla seeds. It’s a great source of omega-3 fatty acids, and it’s estimated that each tablespoon contains nearly 9,000 milligrams of ALA. According to one study out of Tokyo, swapping soybean oil for perilla oil was able to double levels of ALA in the blood, plus increase levels of EPA and DHA in the long run as well. Mix perilla oil into your favorite salad dressings, or add it to cooked vegetable dishes to effortlessly bump up your omega-3 fatty acid intake.
6. Flaxseed
Flaxseed is often considered the best vegan omega-3 food, thanks to both its stellar nutritional profile and versatility. In fact, just one tablespoon of cooked, ground flaxseed provides nearly 1,600 milligrams of ALA.
With its slightly nutty, earthy taste, flaxseed makes a great addition to cereal, oatmeal, smoothies and more. It also works well in baked goods and can be mixed with water for an easy egg substitute.
7. Spirulina
Spirulina is a vegan omega-3 algae that has long been revered for its health-promoting properties. This form of seaweed is rich in many essential nutrients but is an especially good source of omega-3 fatty acids, with about 230 milligrams per ounce.
Not only that, but each serving of spirulina also contains a hearty chunk of protein, riboflavin, iron, copper and thiamine as well. Most commonly available in dried powder form, this incredible ingredient works best mixed into green smoothies alongside other superfoods.
8. Hemp Seeds
Hemp seeds are loaded with vegan omega-3 fatty acids, with approximately 6,000 milligrams of ALA crammed into each one-ounce serving. Available in whole, ground or seed oil varieties, there are plenty of ways to add hemp seed to your daily diet. To get started, try adding hemp seed to smoothies and shakes, mixing it into granola bars and desserts, or sprinkling it over oatmeal for a power-packed breakfast.
Benefits
There are plenty of reasons to make sure you squeeze a few servings of omega-3 vegan foods in your diet each day. Here are a few of the top benefits associated with vegan omega-3:
1. Improves Heart Health
Some research suggests that omega-3 fatty acids can decrease several risk factors for heart disease. In fact, omega-3 fatty acids been shown to reduce diastolic blood pressure and decrease triglyceride levels, both of which play a central role in heart health.
2. Decreases Inflammation
Omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to decrease levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin 6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) in the blood, all of which are considered common markers of inflammation.
3. Boosts Brain Function
Studies show that omega-3 fatty acids may help slow cognitive decline in older adults and may offer protection against dementia and Alzheimer’s disease.
4. Supports Strong Bones
Omega-3 fatty acids are closely involved in bone health and can help increase calcium absorption to prevent bone loss.
5. Enhances Mental Health
Supplementing with omega-3 fatty acids may aid in the treatment of common mental health conditions, such as depression and anxiety.
6. Improves Sleep Quality
Some studies have found a link between increased consumption of omega-3 fatty acids and improved sleep quality in adults.
7. May Protect Against Cancer
Although more research is needed, some research shows that a higher intake of omega-3 fatty acids may be associated with a lower risk of breast, prostate and colorectal cancer.
8. Relieves Joint Pain
In addition to decreasing inflammation, studies show that omega-3 fatty acids can also improve symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, a condition characterized by pain, swelling and stiffness in the joints.
How to Get Vegan Omega-3 Into the Diet
One of the easiest and most effective ways to increase your intake of omega-3 fatty acids is to add more omega-3 foods into your diet. Be sure to fit at least one to two servings into your diet each day by incorporating them into snacks, side dishes and main courses alike.
A smoothie with spirulina, chia seeds and your choices of fruits and veggies, for example, can supply tons of nutrients and can be a great way to start your morning on the right foot. Meanwhile, homemade granola made with walnuts, flaxseed and hemp seeds is a tasty snack idea that can help propel you through the day.
Taking a vegan omega-3 supplement is another easy option to help meet your omega-3 needs. Algal oil is one of the most common vegan omega-3 supplements on the market. It is often favored over other types because it provides DHA and EPA, both of which can be absorbed and used by the body more easily. F
lax oil, hemp oil and perilla oil are also available and can often be found in capsule form for a quick and convenient way to amp up ALA intake.
Supplements and Dosage
So do vegans take fish oil? And if not, what is the best vegan omega-3 supplement? Although fish oil is not vegan-friendly, there are several different vegan omega-3 supplement options out there, including algal oil, perilla oil, hemp oil and flax oil.
The main difference between plant-based omega-3 vs. fish oil, however, comes down to the forms of omega-3s that they contain. While fish and seafood contain both EPA and DHA, the two active forms of omega-3 in the body, most plant-based sources of omega-3 contain ALA, which must be converted to DHA or EPA before it can be used. Unfortunately, studies show that only about 5 percent of ALA is converted to EPA and only around 0.5 percent is actually converted into DHA.
Therefore, the best vegan omega-3 supplement should contain both EPA and DHA for maximum effectiveness. Algae omega-3 supplements, such as spirulina or algal oil, are some of the few plant-based sources on the market that contain these vital essential fatty acids.
How much omega-3 per day? It’s generally recommended to get between 300–900 milligrams of combined EPA and DHA per day. Alternatively, if opting for vegan omega-3 supplements that contain ALA, the dosage recommendations increase to 1,100 milligrams per day for women and 1,600 milligrams daily for men.
Risks and Side Effects
Most vegan omega-3 foods can be safely consumed with minimal risk of adverse side effects. When taking supplements, however, it’s always best to use as instructed to avoid negative effects on health. If you do experience any side effects, consider decreasing your dosage and consult with your doctor to address any concerns.
Additionally, many people wonder: Is vegan omega-3 as good as fish oil? Note that many omega-3 supplements contain mostly ALA, which is converted only in small amounts to DHA and EPA in the body. However, algal oil and spirulina do contain DHA and EPA, and algal oil typically is as well-absorbed and easily tolerated.
Final Thoughts
- There are plenty of vegan foods and supplements available that contain ALA, DHA and EPA to help meet your omega-3 fatty acid needs.
- Some of the top vegan omega-3 foods include Brussels sprouts, algal oil, walnuts, chia seeds, perilla oil, flaxseed, spirulina and hemp seeds.
- Meeting your daily requirements can come with many benefits, such as improved heart health, better brain function, better sleep quality and more.
- There are also plenty of options for plant-based omega-3 supplements, including algal oil, spirulina, perilla oil, hemp oil and flax oil.
- Using a combination of vegan omega-3 foods and/or supplements can make it easy to meet your daily needs of this essential fatty acid.