This Dr. Axe content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure factually accurate information.
With strict editorial sourcing guidelines, we only link to academic research institutions, reputable media sites and, when research is available, medically peer-reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
This article is based on scientific evidence, written by experts and fact checked by our trained editorial staff. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to medically peer-reviewed studies.
Our team includes licensed nutritionists and dietitians, certified health education specialists, as well as certified strength and conditioning specialists, personal trainers and corrective exercise specialists. Our team aims to be not only thorough with its research, but also objective and unbiased.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
Mackerel Fish: Benefits with Cholesterol-Lowering Omega 3’s?
October 26, 2023

One thing that most doctors, dietitians and health professionals are generally able to agree upon across the board is that adding fish to your diet comes with some major benefits to health. In fact, the American Heart Association actually recommends including at least two servings of fatty fish in your weekly diet to help enhance heart health.
Right up there with salmon, tuna and herring fish in terms of nutrition is mackerel fish, a super-nutritious type of fish that’s practically bursting with protein, omega-3 fatty acids and micronutrients.
Plus, with some research indicating that regular consumption could help drop your blood pressure and cholesterol, minimize your waistline, protect against depression, and keep your bones healthy and strong, mackerel fish definitely makes a great addition to any healthy, well-balanced diet.
What Is Mackerel?
So what is a mackerel fish? If you frequent sushi bars, you may know it as saba fish. You may have also unknowingly passed by it in the grocery store, sitting right next to the canned anchovies and sardines.
Mackerel is a family of saltwater fish composed of over 30 different species, including popular varieties like Atlantic mackerel, Pacific mackerel, Spanish mackerel and king mackerel fish.
Available both fresh and canned, mackerel is a favorite among fish lovers thanks to its versatility, flavor and incredible nutrient profile.
Nutrition Facts
Mackerel fish is a very nutrient-dense food and packs in tons of protein, omega-3 fatty acids and micronutrients for a low amount of calories. In particular, mackerel is especially high in vitamin B12, selenium, niacin and phosphorus, among a range of other essential vitamins and minerals.
One four-ounce (112 g) serving of raw Atlantic mackerel contains approximately:
- 230 calories
- 20.8 grams protein
- 15.6 grams fat
- 16.1 micrograms vitamin B12 (269 percent DV)
- 720 IU vitamin D (120 percent DV)
- 43.9 micrograms selenium (63 percent DV)
- 5.8 milligrams niacin (29 percent DV)
- 236 milligrams phosphorus (24 percent DV)
- 82.5 milligrams magnesium (21 percent DV)
- 0.4 milligram riboflavin (21 percent DV)
- 0.4 milligram vitamin B6 (20 percent DV)
- 341 milligrams potassium (10 percent DV)
- 0.1 milligram thiamine (9 percent DV)
- 0.8 milligram pantothenic acid (8 percent DV)
- 1.3 milligrams iron (7 percent DV)
In addition to the nutrients listed above, mackerel also contains some zinc, copper and vitamin A.
Benefits
1. Aids in Lowering Blood Pressure
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a common condition that affects millions of people around the world. When your blood pressure is too high, it forces the heart to work harder to pump blood, increasing the risk of heart disease. Mackerel fish is known for its ability to boost heart health and slash blood pressure.
A study published in Atherosclerosis demonstrated this by supplementing 12 men with high blood pressure with three cans of mackerel daily for eight months, which resulted in a significant decline in blood pressure. Another review compiled the results of several studies and concluded that adding a few servings of mackerel into the diet per day can lead to long-term reductions in blood pressure.
Some other natural ways to lower blood pressure include reducing your sodium intake, eating more fiber-rich foods and upping your intake of magnesium and potassium.
2. Can Help Reduce Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a type of fat that is found throughout your body. While you do need cholesterol, too much can build up in your blood and cause your arteries to narrow and harden. Including mackerel in your diet may help improve heart health by lowering cholesterol levels.
In one study comprising 15 volunteers, eating mackerel for two weeks was found to decrease levels of both triglycerides and total cholesterol in the blood. Meanwhile, another study in India looked at the diets of 1,000 adults and found that the average cholesterol levels of fish consumers was lower than non-fish consumers.
You can also lower cholesterol naturally by limiting your intake of processed junk, getting in regular physical activity and trying out some simple stress relievers.
3. Helps Fight Against Depression
Mackerel is high in omega-3 fatty acids, a healthy type of fat that has been associated with a number of impressive health benefits. Mackerel provides both EPA and DHA, two types of essential fatty acids that the body uses for better brain function. In fact, some recent research has even found that omega-3 fatty acids may even be able to help protect against depression.
A review published in the journal CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics looked at the results of three studies and showed that omega-3 fatty acids were able to reduce depressive symptoms by up to 50 percent in those with major depression, bipolar disorder and childhood major depression. Not only that, but other studies have found an association between lower intakes of omega-3 fatty acids and depressive symptoms.
Spending more time outdoors, eating plenty of probiotic-rich foods and following a well-balanced diet are some other effective natural remedies for depression that you can try.
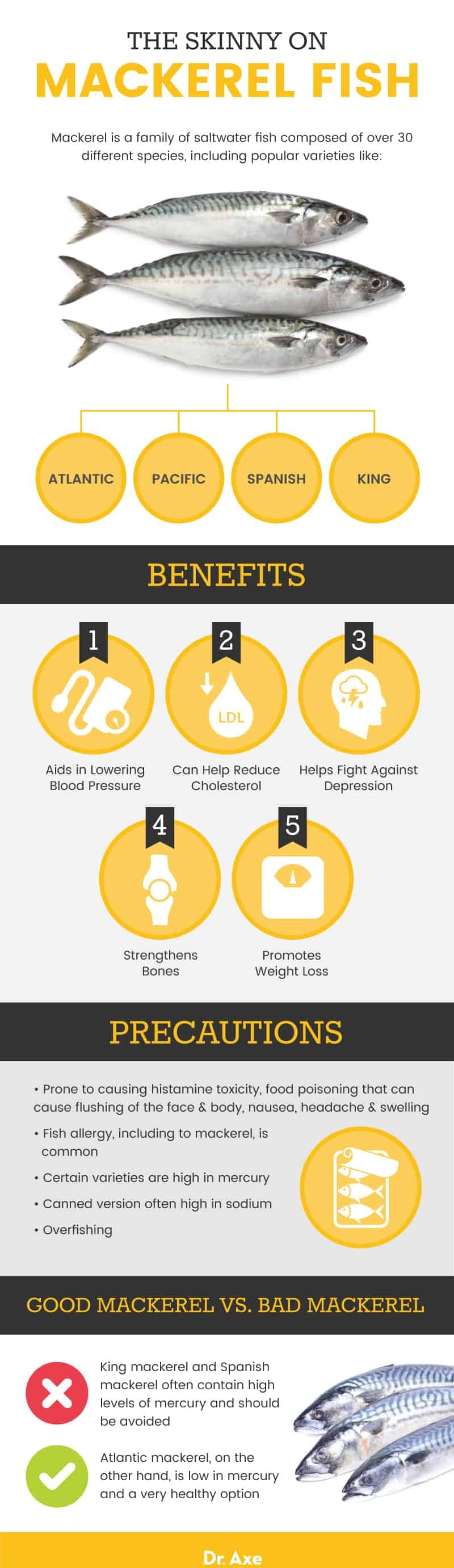
4. Strengthens Bones
Like other types of oily fish, mackerel is a vitamin D-rich food. Vitamin D is an incredibly important nutrient, but it can be challenging to meet your needs without supplementation. In fact, an estimated 50 percent of the population worldwide is believed to have a vitamin D deficiency.
Vitamin D is key to many aspects of health, but it’s especially crucial when it comes to bone health. It aids in the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus and is essential to supporting the growth of stronger bones. Plus, according to a 2013 study, postmenopausal women with low levels of vitamin D in the blood are at greater risk for bone loss, frailty and fracture compared to those with sufficient levels of serum vitamin D.
Including other fatty fish in your diet, such as halibut, carp fish and salmon, can also bump up your vitamin D intake and help you meet your daily needs.
5. Promotes Weight Loss
Mackerel is rich in healthy fats and proteins, which can keep you feeling full and help amp up weight loss. Studies have found that both protein and fat decrease levels of the ghrelin, the hormone that stimulates hunger, more than carbohydrates. Research also shows that high-protein diets can increase satiety as well as thermogenesis, or the amount of calories burned by the body after eating.
With 20 grams of protein, 15 grams of fat and zero carbs per serving, mackerel can be an excellent addition to a weight loss diet. However, be sure to pair it with other high-protein and high-fiber foods to achieve maximum results.
Your Guide to Mackerel Fish
With over 30 species of mackerel, it can be challenging to know which kind to get when you’re standing at the grocery store.
King mackerel has been shown to have high levels of mercury, which can be dangerous in high amounts and can even cause mercury poisoning. Spanish mackerel may have elevated levels of mercury as well and should be limited, especially by women who are nursing or pregnant. Instead, opt for a type like Atlantic mackerel, which is low in mercury but still contains a concentrated dose of omega-3 fatty acids and protein.
Keep in mind that Pacific jack mackerel, horse mackerel and mackerel pike, three types of fish that are commonly used to prepare sushi, are actually unrelated to mackerel. In fact, they belong to other families of fish entirely.
Although mackerel can be purchased fresh from fish markets, buying it canned is a convenient and popular choice. If purchasing canned, be sure to look for a brand that uses BPA-free cans to avoid the toxic effects of BPA. Additionally, most canned foods are often preserved in high amounts of salt, so make sure you rinse well before chowing down.
Wondering how to cook mackerel? Canned mackerel can actually be eaten cold on salads, mashed and spread on toast, or paired with your choice of veggies. You can also try baking, roasting or grilling your fish — fresh or canned —for a warm and delicious main course. Mackerel also makes a great addition to dishes like curry, pâté, kedgeree or risotto.
Precautions
Some people may have an allergy to fish and should avoid consuming mackerel. Mackerel is also prone to causing histamine toxicity, a form of food poisoning that can result in symptoms like flushing of the face and body, nausea, headache and swelling. If you experience any adverse side effects or food allergy symptoms after eating mackerel, you should discontinue use and talk to your doctor.
Although mackerel is associated with plenty of health benefits, not all mackerel is great for your health. In fact, King mackerel is high in mercury and even makes the list of fish you should never eat. Instead, select varieties like Atlantic mackerel, which are low in mercury.
Additionally, pregnant women should carefully monitor their intake of mercury to reduce the risk of developmental delays and birth defects. While certain types like Atlantic mackerel are low in mercury and safe to eat on a pregnancy diet, fish should be limited to one or two times per week as part of an otherwise healthy, well-balanced diet.
If buying canned, be sure to rinse thoroughly to remove excess salt. Canned varieties are usually high in sodium, which can contribute to high blood pressure and other health problems for some individuals.
Another concern with mackerel is overfishing and its potential environmental impact. Like several other species of fish, mackerel has been overfished to the point where it is on the brink of extinction, which could have a massive effect on the ecosystem of the ocean. By being informed about which types of mackerel are most sustainable, you can minimize your contribution to this growing problem while still taking advantage of the many health benefits. Monterey Bay Aquarium’s Seafood Watch has a free tool that helps you find the best and most sustainable choice in terms of type, fishing method and location.
Final Thoughts
- Mackerel is an excellent source of protein, omega-3 fatty acids, and numerous important vitamins and minerals.
- The nutrients found in mackerel could aid in lowering blood pressure and cholesterol levels, fighting against depression, improving bone health, and increasing weight loss.
- It’s also important to pick varieties that are sustainable and contain low levels of mercury to optimize the environmental and health impacts of this nutritious fish.
- Try mackerel grilled, roasted, baked or even straight out of the can as part of a tasty salad, snack, side dish or main course.










