This Dr. Axe content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure factually accurate information.
With strict editorial sourcing guidelines, we only link to academic research institutions, reputable media sites and, when research is available, medically peer-reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
This article is based on scientific evidence, written by experts and fact checked by our trained editorial staff. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to medically peer-reviewed studies.
Our team includes licensed nutritionists and dietitians, certified health education specialists, as well as certified strength and conditioning specialists, personal trainers and corrective exercise specialists. Our team aims to be not only thorough with its research, but also objective and unbiased.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
Best Omega-6 Foods, Surprising Benefits & Proper Ratio with Omega-3s
November 29, 2018

There’s an essential fatty acid that is necessary for optimal health but cannot be produced on its own by the body. I’m talking about omega-6.
Omega-6 fatty acids, like omega-3s, are essential fatty acids that can only be obtained through food and supplements. But even though this healthy fat is not produced in the body at all, omega-6 fatty acids are very important to the brain and play an integral role in growth and development.
This polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) does so much more than just keep the brain in good order, however. It also stimulates skin and hair growth, maintains good bone health, helps regulate metabolism, keeps the reproductive system healthy and does so much more.
So are omega 6 fatty acids good for you or is omega 6 inflammatory? Here’s what you need to know about this essential fatty acid and how it affects your health.
Benefits of Omega-6
1. Helps Reduce Nerve Pain
Studies show that taking gamma linolenic acid (GLA) — a type of omega-6 fatty acid — may reduce symptoms of nerve pain in people with diabetic neuropathy long-term. (1) Diabetic neuropathy is a type of nerve damage that can occur as a result of poorly controlled diabetes. One study in the journal Diabetes Care actually found that taking GLA for one year was significantly more effective at decreasing symptoms of diabetic neuropathy than a placebo. (2) Although more research is needed, this could have far-reaching effects and may be beneficial for people with a variety of conditions that cause nerve pain, including cancer and HIV.
2. May Treat Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder characterized by rheumatoid arthritis symptoms such as joint pain, stiffness and swelling. Although traditional treatment typically involves the use of prescription medications and physical therapy, certain types of omega-6 fatty acids may actually help reduce symptoms and keep joint pain at bay.
Evening primrose oil, in particular, comes from the seeds of a Native American wildflower and contains 7 percent to 10 percent GLA. Preliminary evidence suggests that evening primrose oil may reduce pain, swelling and morning stiffness. (3) It can take up to six months to notice the effects but may not actually stop the progression of the disease, which means that joint damage can still occur.
To treat rheumatoid arthritis, the Arthritis Foundation suggests taking between 540 milligrams to 2.8 grams of evening primrose oil daily in divided doses, but it’s recommended to check with your doctor first before starting supplementation. (4)
3. May Help Reduce Symptoms of ADHD
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, also known as ADHD, is a condition that can affect both children and adults and can cause symptoms like limited attention, hyperactivity, impulsivity and mood swings.
One study out of Sweden focused on treating subjects with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) using omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acid supplementation. The study included a total of six months of testing with 75 children and adolescents. While a majority did not respond to omega-3 and omega-6 treatment, a subgroup of 26 percent responded with more than a 25 percent reduction of ADHD symptoms. After six months, 47 percent showed improvement in symptoms. (5)
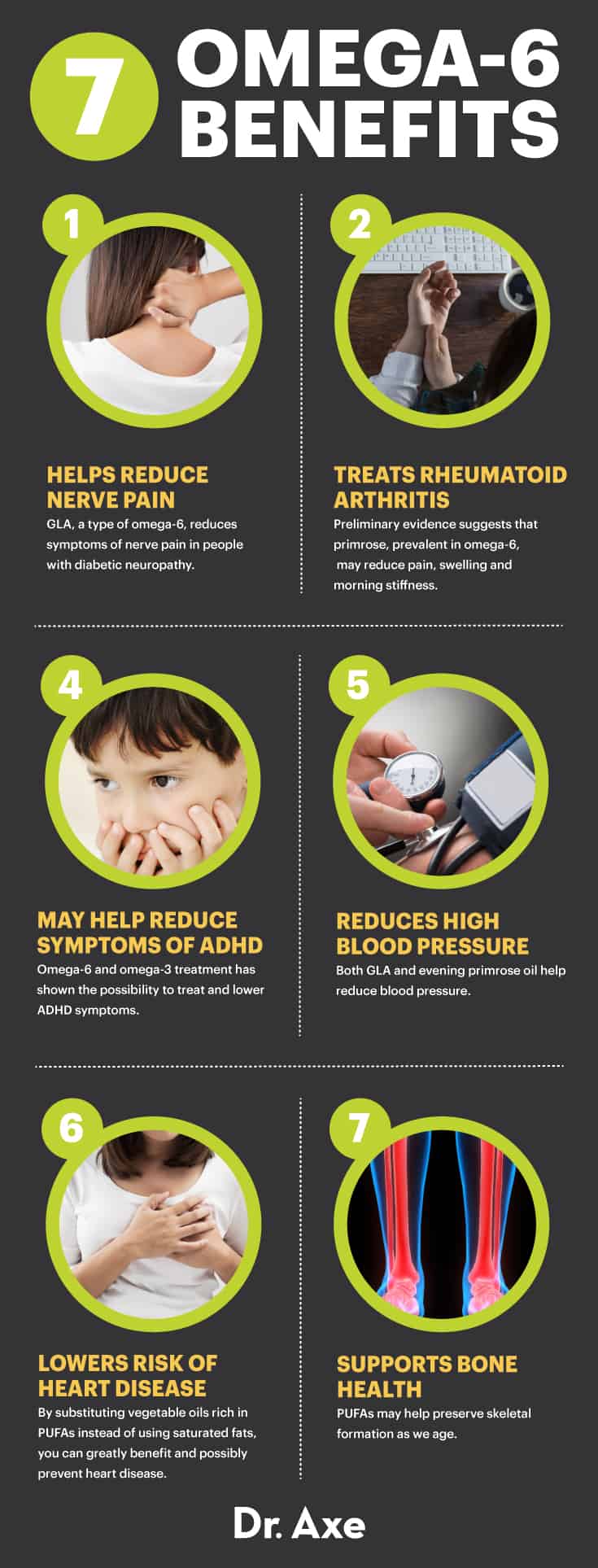
4. Reduces Blood Pressure
High blood pressure is a serious condition that can increase the force of the blood against the artery walls, putting extra strain on the heart muscle and causing it to weaken over time.
Studies show that GLA alone or combined with omega-3 fish oil may help reduce high blood pressure symptoms. In fact, one study of men with borderline high blood pressure showed that taking blackcurrant oil, a type of oil that is high in GLA, was able to significantly reduce diastolic blood pressure compared to a placebo. (6)
5. Lowers Risk of Heart Disease
Health organizations like the American Heart Association often recommend substituting vegetable oils rich in polyunsaturated fats like linoleic acid in place of saturated fats to decrease the risk of coronary heart disease. (7)
Of course, keep in mind that some choices are better than others when it comes to vegetable oils, as many are often highly refined and derived from genetically modified crops, which top the list of omega 6 foods to avoid. However, linoleic acid can also be obtained from other sources as well, including nuts and seeds. Walnuts, in particular, are a great source of omega-6s, providing about 11 grams of linoleic acid as well as a good amount of alpha-linolenic acid, a plant-based omega-3 fatty acid that can help keep your fatty acid intake balanced.
6. Supports Bone Health
As we get older, we start to slowly lose bone tissue over time, resulting in an increased risk of fractures and falls. Studies conducted in Southern California and published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition indicate that PUFAs may help preserve skeletal formation as we age, reporting that both men and women showed improvement in the bones of the hips and spine when taking omega-6 and omega-3 fats.
Furthermore, the ratio of these essential fatty acids may also come into play. Researchers reported that eating a higher ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 fatty acids was associated with lower bone mineral density in the hips for both sexes, suggesting that keeping your intake in balance is just as crucial as including both fatty acids in your diet. (8)
Foods and Supplements
So what foods are high in omega 6? There are several different types of omega-6 fatty acids, and most come from vegetable oils, such as linoleic acid. Linoleic acid is converted to GLA in the body. From there, it breaks down even more to what’s known as arachidonic acid. GLA can be found in several plant-based oils, including evening primrose oil, borage oil and black currant seed oil.
Beef, chicken, eggs, nuts and seeds are also great sources of omega-6 fatty acids. However, it’s important to opt for organic, unprocessed and non-GMO whole foods whenever possible to maximize the potential omega 6 benefits.
Omega-6 supplements are also available, but it’s always best to get the nutrients that the body needs through food sources instead. Not only do these nutritious omega 6 fatty acids foods help supply your body with the essential fats that you need, but they also contain a wealth of important vitamins, minerals and antioxidants as well.
Here is a list of the different types of omega-6 fatty acids and where you can obtain them:
- Linoleic Acid: soybean oil, corn oil, safflower oil, sunflower oil, peanut oil, cottonseed oil, rice bran oil
- Arachidonic Acid: peanut oil, meat, eggs, dairy products
- GLA: hemp seeds, spirulina, evening primrose oil, borage oil, black currant seed oil
Highest Omega-6 Foods: (9)
- Safflower
- Grapeseed
- Sunflower oil
- Poppyseed oil
- Corn oil
- Walnut oil
- Cottonseed oil
- Soybean oil
- Sesame oil

Recipes
Looking for some healthy ways to get in your fix of these essential fatty acids? You can easily swap some healthy oils into your favorite recipes or sprinkle nuts and seeds over salads, smoothies or cereals to squeeze in your daily dose. Need a few more ideas? Here are a few nutritious recipes to get you started:
- Mango Walnut Spinach Salad
- Easy Chana Masala
- Spicy Roasted Pumpkin Seeds
- Poppy Seed Overnight Oats
- Egg Tahini Salad
History/Facts
Although researchers now are well-aware of the powerful impact that fatty acids can have on health, the significance of dietary fat wasn’t fully realized until the 1900s. In fact, before then, dietary fat was only used as a simple way to increase caloric intake and promote weight gain.
Omega-6 fatty acids were first discovered in 1929 by George and Mildred Burr, a husband and wife duo that conducted research on rats showing that a lack of fatty acids in the diet could cause deficiency and, in extreme cases, even death. Not only did this lead to the discovery of omega-6 fatty acids, but it also demonstrated the importance of other essential fatty acids, such as omega-3 fatty acids. (10)
However, up until fairly recently, linoleic acid was considered the only essential fatty acid required to obtain through dietary sources and was the only fatty acid required to be added to infant formula until the mid-1990s. (11) Scientists now recognize two types of essential fatty acids that your body is unable to synthesize: linoleic acid and alpha-linolenic acid.
Today, researchers are continuing to learn about the many ways that essential fatty acids like omega-6 can influence health, plus the importance of maintaining proper balance of fatty acids to fight inflammation and prevent chronic disease.
Risks and Side Effects
Unfortunately, the typical American diet tends to contain significantly more omega-6 fatty acids than omega-3 fatty acids, particularly because omega-6 is in a lot of unhealthy foods, such as salad dressings, potato chips, pizza, pasta dishes and processed meats like sausage, to name a few.
So why is omega 6 bad when it’s consumed in high amounts? Excessive consumption of vegetable oils, or linoleic acids, can contribute to inflammation and increase the risk of serious conditions like heart disease, cancer, asthma, arthritis and depression, which is one reason why you should keep your intake in moderation.
On the other hand, these fatty acids are absolutely vital to maintaining overall health, so you shouldn’t cut them out of your diet altogether. Instead, aim for a balance of omega 3 and omega 6 foods in your diet and steer clear of unhealthy sources of omega-6 fatty acids, including processed junk. Although the average western diet contains an omega 6 vs omega 3 ratio of around 15:1, the suggested ratio should actually be closer to around 2:1 for optimal health. (12)
People with specific conditions, such as eczema, psoriasis, arthritis, diabetes or breast tenderness, should consult their doctors before taking any omega-6 supplements. Both borage oil and evening primrose oil reportedly lower the seizure threshold, so individuals requiring anticonvulsant medication should exercise caution and discuss it with their physician.
Final Thoughts
- Omega-6 is an essential fatty acid we must obtain from food and supplement sources, since our bodies do not produce it on their own.
- So is omega 6 good or bad? Omega-6 fatty acids come with a number of important health benefits and can help reduce nerve pain, decrease arthritis symptoms, treat symptoms of ADHD, lower blood pressure, reduce the risk of heart problems and supports bone health.
- Some of the top omega-6 foods include safflower, grapeseed, sunflower oil, poppyseed oil, corn oil, walnut oil, cottonseed oil, soybean oil and sesame oil.
- Most Americans consume too many omega-6s and not enough omega-3s. Researchers studying the link between omega 6 and inflammation recommend balancing the ratio between omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids for optimal health.










